ទិដ្ឋភាពទូទៅនៃ pH
1. តើ pH គឺជាអ្វី?
pH គឺជាខ្នាតសម្រាប់វាស់កំហាប់ទាក់ទងគ្នានៃអ៊ីយ៉ុងអ៊ីដ្រូសែន (H+) និងអ៊ីយ៉ុងអ៊ីដ្រុកស៊ីត (OH−) នៅក្នុងសូលុយស្យិងទឹក។ ខ្នាត pH មានចាប់ពី 0 ដល់ 14៖
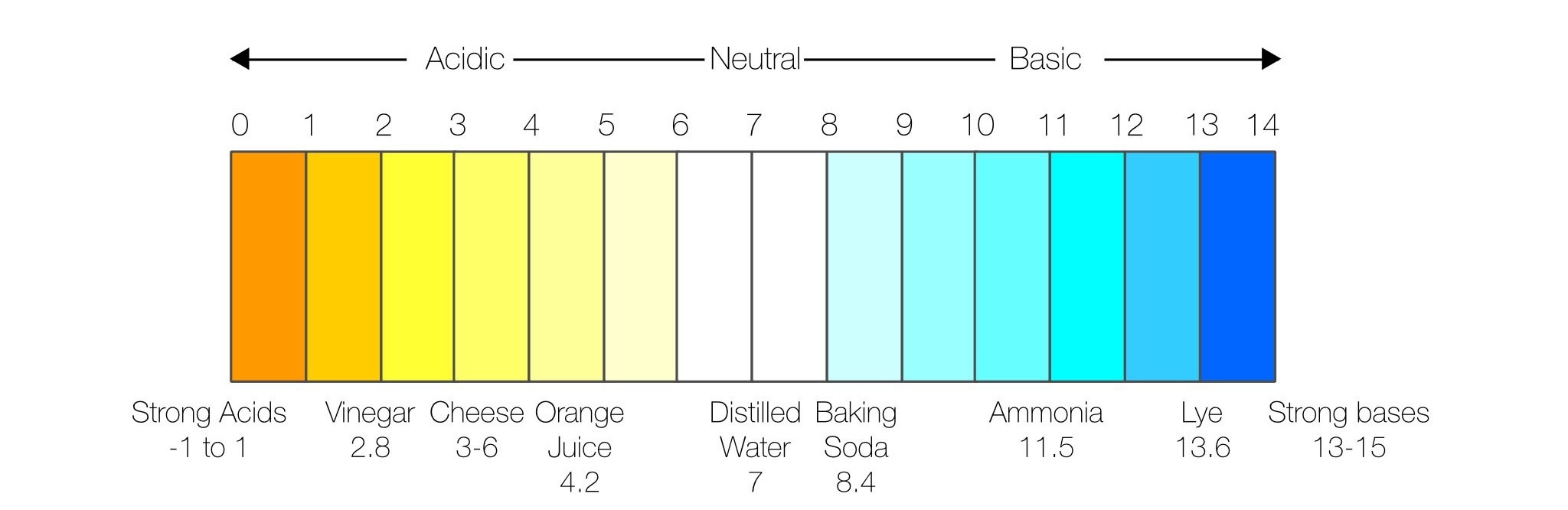
2. ហេតុអ្វីការវាស់ pH មានសារៈសំខាន់?
ការវាស់ pH ជួយវាយតម្លៃពីគុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ជីវិតរុក្ខជាតិ និងសត្វក្នុងទឹក។ ប្រសិនបើទឹកក្លាយជាអាស៊ីត ឬបាសខ្លាំងពេកដោយសារតែកត្តាបំពុល (ធម្មជាតិ ឬមនុស្សបង្កើត) វានឹងអាចបង្កផលប៉ះពាល់អវិជ្ជមានយ៉ាងធ្ងន់ធ្ងរដល់ជីវិតក្នុងទឹក។
តម្លៃ pH ដែលចាត់ទុកថាធម្មតានៅក្នុងប្រភពទឹកជាទូទៅស្ថិតនៅចន្លោះ 5.0 ដល់ 9.0 ប៉ុន្តែតម្លៃល្អបំផុតគឺនៅចន្លោះ 6.0 ដល់ 8.0។
3. វិធីសាស្រ្តវាស់ pH
វិធីសាស្រ្តវាស់ pH ទូទៅដូចជា ឧបករណ៍តេស្តគីមី និងក្រដាស pH (pH strips) គឺសាមញ្ញ និងមានតម្លៃថោក។ ទោះជាយ៉ាងណាក៏ដោយ វិធីសាស្ត្រទាំងនេះអាចផ្តល់លទ្ធផលមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ ដោយសារវាផ្អែកលើការប្រែប្រួលពណ៌។
វិធីសាស្ត្រវាស់ pH ដែលមានភាពត្រឹមត្រូវជាងគឺការប្រើប្រាស់ ឧបករណ៍វាស់ pH (pH meter)។ នៅពេលជ្រើសរើសឧបករណ៍នេះ លោកអ្នកគួរពិចារណាលើទាំងអេឡិចត្រូត និងតួឧបករណ៍ ដើម្បីធានាថាវាស័ក្តិសមបំផុតសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់នៅទីតាំងជាក់ស្តែង។
ឧបករណ៍វាស់ pH ជំនាញសម្រាប់អ្នកដើម្បីទទួលបានភាពត្រឹមត្រូវដូចនៅក្នុងមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍នៅទីតាំងជាក់ស្តែង លោកអ្នកអាចស្វែងយល់ពីឧបករណ៍វាស់ចម្រុះមួយចំនួនរបស់ Hanna Instruments ដែលអាចវាស់ pH និងប៉ារ៉ាម៉ែត្រជាច្រើនទៀតដោយភាពត្រឹមត្រូវ និងប្រសិទ្ធភាព។ ឧបករណ៍ដែលមានលេខកូដដូចជា HI9829, HI98194, HI98193 និង HI98190 គឺជាជម្រើសដ៏គួរឱ្យទុកចិត្តសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញ។
4. ការក្រិត pH នៅទីតាំង
ការក្រិត គឺជាជំហានសំខាន់ដើម្បីធានានូវភាពត្រឹមត្រូវ។ លោកអ្នកគួរជ្រើសរើសសូលុយស្យុងប៊ូហ្វែ (buffer) ដែលមានតម្លៃជុំវិញតម្លៃ pH ដែលអ្នករំពឹងទុក។
5. នីតិវិធីនៃការក្រិត
ដើម្បីស្វែងយល់លម្អិតបន្ថែម សូមពិនិត្យមើលនីតិវិធីប្រតិបត្តិស្តង់ដារ (SOP) របស់យើងសម្រាប់ការវាស់វែង pH។ pH Measurement SOP.
pH is a measurement of the relative concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in water. The scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being a strong acidic solution and 14 being strongly basic.

pH is a way to evaluate the suitability of water for living plant and animal organisms. If water has become too acidic or basic due to natural or man-made pollutants, there can be a profound negative impact on aquatic life. pH is considered normal in a body of water if it has a value of 5.0 to 9.0, but ideally it would fall in the range of 6.0 to 8.0.
Common pH tests, like chemical test kits and pH strips, are simple and inexpensive. However, they come with some issues that could lead to inaccurate results. Both of these methods of testing pH give you results based on a chemical reaction that results in a color change. When your paper or liquid sample changes color, you match it to the color guide provided and get your pH reading.
A more accurate means of testing pH is using a pH meter. When choosing a pH tester or meter, there are a number of considerations related to both the electrode as well as the device. Be sure to find a pH meter and electrode that is best suited for field work.
The first thing is to choose the buffer solutions that will bracket your expected value. What is bracketing? Also known as a two-point or multi-point calibration, bracketing consists of calibrating to two pH points – one above and one below your desired pH range. For example, if you want to measure the pH of lemon juice, which has a pH around 2, you could use technical buffers 1.00 and 4.01 for a two-point calibration. If the pH of your water sample is unknown, then a third calibration point will ensure the best accuracy.
Calibration Procedure
Check out our full pH Measurement SOP.
To empower customers to achieve quality
by supplying intuitive, accurate, and reliable analytical instruments with exceptional customer service and value.
We take pride in every product we build. From an original idea, to a completed product ready for testing. We oversee every aspect of the manufacturing process. It is this level of attention to detail that sets us apart.
To empower customers to achieve quality by supplying intuitive, accurate, and reliable analytical instruments with exceptional customer service and value.
We take pride in every product we build. From an original idea, to a completed product ready for testing. We oversee every aspect of the manufacturing process. It is this level of attention to detail that sets us apart.
To empower customers to achieve quality by supplying intuitive, accurate, and reliable analytical instruments with exceptional customer service and value.
We take pride in every product we build. From an original idea, to a completed product ready for testing. We oversee every aspect of the manufacturing process. It is this level of attention to detail that sets us apart.